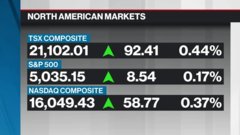
Apr 17, 2024
Boeing Critic Says He Shared Missing 737 Bolt Records With FBI
, Bloomberg News

(Bloomberg) -- A prominent critic of Boeing Co. contradicted the planemaker’s assertion that no records exist of work done on a fuselage panel that later blew off of a 737 Max 9 mid-flight earlier this year.
Ed Pierson, a former Boeing employee who now runs a safety foundation, told a Senate subcommittee on Wednesday that there are documents detailing the work, and that he’s shared them with federal investigators in the wake of the near-tragedy on an Alaska Airlines flight. The accident triggered a crisis of confidence over quality at the company.
“Records do exist documenting in detail the hectic work done on the Alaska Airlines airplane, and Boeing’s corporate leaders know it too,” Pierson said. “I know this Alaska airplane documentation exists because I personally passed it to the FBI.”
The company referred all questions to the National Transportation Safety Board, which is investigating the cause of the Jan. 5 accident. Agency investigators have said the panel was missing four bolts that hold it in place when it left Boeing’s factory.
The NTSB has received no documentation detailing the opening, closing or securing of that door plug from Boeing “or any other entity,” an NTSB spokesman said.
Boeing maintains it has no formal log of the repairs done that required opening the door plug — a serious violation of its own manufacturing procedures — and thus can’t pinpoint who did the work. Without written work orders, the company’s quality inspectors wouldn’t have known to check on the repair, or spot the missing bolts.
Twin logs — one which officially tracks every action taken as the plane is put together, and another less formal factory communication tool — appear to have led to confusion at Boeing’s factory in Renton, Washington, Bloomberg has reported.
Read More: Boeing Record Systems Eyed in 737 Max Door Plug Blowout
In testimony to Congress on April 10, NTSB Chair Jennifer Homendy said that Boeing has “provided us with all the documents that we’ve asked for that exist, they are aware that this record does not exist.”
Pierson first sounded alarms on sloppy manufacturing practices on the 737 Max in the aftermath of two deadly crashes in 2018 and 2019. He was harshly critical of Boeing’s handling of the latest crisis involving the company’s top-selling plane.
He told the committee on Wednesday that the records on the Alaska Airlines door plug were provided to him by an internal whistleblower at Boeing, and that they have been available for months. “In my opinion this is a criminal cover-up,” Pierson said at the hearing.
Read More: Boeing Fired Lobby Firm That Helped It Navigate 737 Max Crashes
The alarming near-miss has sparked a criminal investigation by the Justice Department, which has convened a grand jury. The Federal Aviation Administration has capped 737 production until it’s confident Boeing has a handle on quality, and given the company until late May to draft a plan for improving its manufacturing processes.
“I don’t think there’s anyone at Boeing from Dave Calhoun down that doesn’t want to know what happened here,” Homendy said last week, referring to Boeing’s chief executive officer. “They want to know, and they want to fix it.”
--With assistance from Allyson Versprille.
(Updates with NTSB statement in fifth paragraph)
©2024 Bloomberg L.P.