Nov 26, 2021
Traders unwind rate-hike bets as new COVID fears spread
, Bloomberg News
Expect similar interest rate market behavior in 2022 akin to 2014: Dennis Mitchell
Money markets are offloading bets on central bank interest-rate hikes in a hurry, as inflation fears give way to concerns that a new coronavirus strain may spread globally and slow economic growth.
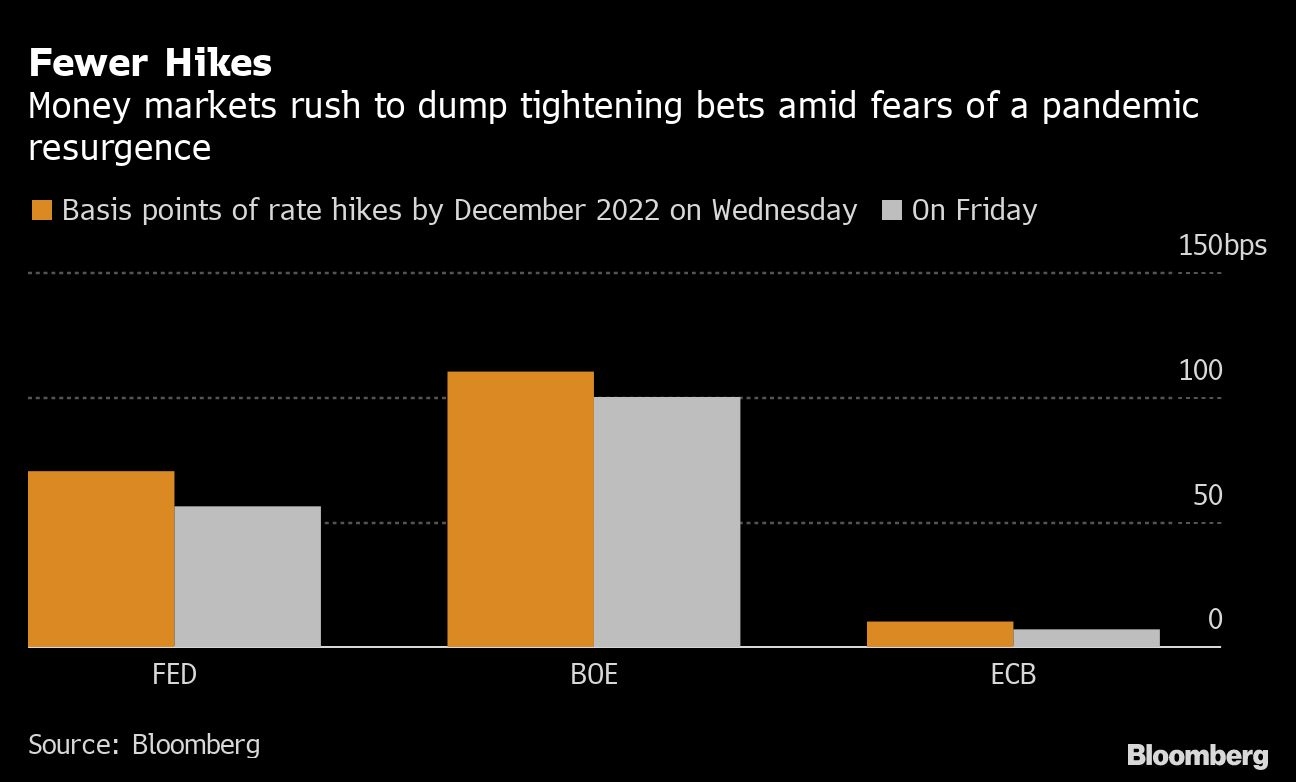
Traders have pushed back the timing of a 25-basis-point rate increase by the Federal Reserve to September from June, with only one further hike expected for the remainder of 2022. It’s a similar story in the U.K. where the Bank of England is now expected to tighten policy in February instead of next month.
Wagers that the European Central Bank will raise its deposit rate by the end of next year have also been slashed, with only a seven basis-point increase priced in, around half of that seen earlier this week. The European Union is proposing to follow the U.K. in halting air travel from southern Africa after the new COVID-19 variant was identified there.
“Over the next couple of weeks we could see this move continuing,” said Pooja Kumra, senior European rates strategist at Toronto-Dominion Bank, in an interview on Bloomberg Television. “Right now we would expect central banks to remain more sympathetic to the situation before removing any accommodation.”
Major central banks have spent months priming the market for an era of tighter monetary policy as the global economy emerged from the pandemic and inflation accelerated. Yet the prospect of widespread travel restrictions and renewed curbs to social activity mean policy makers have to think twice before starting to pull back on support, dealing a blow to traders positioned for rate increases.
The World Health Organization and scientists are studying the recently identified variant, which has been described as very different to previous versions and of serious concern. The U.K., Singapore and Israel curbed travel from South Africa and some neighboring countries. Hong Kong confirmed two cases of the strain.
If the new strain turns out to be as potent as it seems, it “will negate the need for monetary tightening that most developed market central banks were leaning towards,” said Peter Chatwell, multi-asset strategist at Mizuho International Plc. He expects central banks to push back interest-rate hikes by about six months in this instance.
Five-year government bond yields, which are most sensitive to monetary policy, led declines in the U.S. and U.K., falling as much as 15 basis points to 1.19 per cent and 14 basis points to 0.60 per cent, respectively.
Traders are also pushing back of bets for monetary tightening in central and eastern Europe, among the first regions to react to a spike in prices with interest-rate increases this year. Forward-rate agreements over the next 12 months in Hungary, Poland and the Czech Republic tumbled more than 20 basis points.